The way the Kenyan government rules and governs itself has improved greatly since the country achieved independence in 1963. The country has undergone five major constitutional reforms: one in 1963, one in 1977, one in 1991, one in 2000, and lastly, in 2010, which is currently in use.
The newly established constitution aimed at bringing government services closer to the people, and thus, devolved governments, “Also Counties,” were born as a result. Article 174 of the Kenyan constitution provides a framework by which the County governments operate; among them are fostering national unity, giving the powers of self-governance closer to the people, enhancing checks and balances, and separating powers.
As of 2025, there are 47 counties in Kenya, but you may be surprised that not all Kenyans can name the counties and even state who heads them. Therefore, this guide will walk you through everything about Kenyan countries.
List of 47 Counties in Kenya
Before the amendment of the 2010 constitution, the country was unified by 8 provinces, but since the 2010 condition was promulgated, these provinces have been abolished, and 47 counties have been formed.
All the counties in Kenya are liked or identified using a code numbered from 001 to number 047 as follows :
| Code | County | Headquarters/Capital | Governor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | Mombasa | Mombasa | Abdullswamad Nassir |
| 002 | Kwale | Kwale | Fatuma Achani |
| 003 | Kilifi | Kilifi | Gideon Mung’aro |
| 004 | Tana River | Hola | Dhadho Godhana |
| 005 | Lamu | Lamu | Issa Timamy |
| 006 | Taita–Taveta | Mwatate | Andrew Mwadime |
| 007 | Garissa | Garissa | Nathif Jama |
| 008 | Wajir | Wajir | Ahmed Abdullahi |
| 009 | Mandera | Mandera | Mohamed Adan Khalif |
| 010 | Marsabit | Marsabit | Mohamud Ali |
| 011 | Isiolo | Isiolo | Abdi Hassan Guyo |
| 012 | Meru | Meru | Kawira Mwangaza |
| 013 | Tharaka-Nithi | Kathwana | Muthomi Njuki |
| 014 | Embu | Embu | Cecily Mbarire |
| 015 | Kitui | Kitui | Julius Malombe |
| 016 | Machakos | Machakos | Wavinya Ndeti |
| 017 | Makueni | Wote | Mutula Kilonzo |
| 018 | Nyandarua | Ol Karau | Moses Badilisha Kiarie |
| 019 | Nyeri | Nyeri | Mutahi Kahiga |
| 020 | Kirinyaga | Kerugoya | Anne Waiguru |
| 021 | Murang’a | Murang’a | Irungu Kang’ata |
| 022 | Kiambu | Kiambu | Kimani Wamatangi |
| 023 | Turkana | Lodwar | Jeremiah Lomurkai |
| 024 | West Pokot | Kapenguria | Simon Kachapin |
| 025 | Samburu | Maralal | Jonathan Lati Leleliit |
| 026 | Trans-Nzoia | Kitale | George Natembeya |
| 027 | Uasin Gishu | Eldoret | Jonathan Bii Chelilim |
| 028 | Elgeyo-Marakwet | Iten | Wisley Rotich |
| 029 | Nandi | Kapsabet | Stephen Sang |
| 030 | Baringo | Kabarnet | Benjamin Cheboi |
| 031 | Laikipia | Rumuruti | Joshua Irungu |
| 032 | Nakuru | Nakuru | Susan Kihika |
| 033 | Narok | Narok | Patrick Ole Ntutu |
| 034 | Kajiado | Kajiado | Joseph Ole Lenku |
| 035 | Kericho | Kericho | Erick Kipkoech Mutai |
| 036 | Bomet | Bomet | Hillary Barchok |
| 037 | Kakamega | Kakamega | Fernandes Barasa |
| 038 | Vihiga | Mbale | Wilber K. Ottichilo |
| 039 | Bungoma | Bungoma | Ken Lusaka |
| 040 | Busia | Busia | Paul Otuoma |
| 041 | Siaya | Siaya | James Orengo |
| 042 | Kisumu | Kisumu | Anyang’ Nyong’o |
| 043 | Homa Bay | Homa Bay | Gladys Wanga |
| 044 | Migori | Migori | Ochillo Ayacko |
| 045 | Kisii | Kisii | Simba Arati |
| 046 | Nyamira | Nyamira | Amos Nyaribo |
| 047 | Nairobi | Nairobi | Johnson Sakaja |
How does the County government work in Kenya?
The New 2010 Constitution brought some changes in Kenya’s governance structure. Its main goal was to bring services closer to Common “Mwananchi” like you and me through devolution
In general, the county government’s purposes are not just centered around devolution but as well as many other functions, which include:
- Establish the county government and legislate the laws as required by Article 185 of the constitution.
- Performs all the functions distributed to it by the national government and implements all the laws of the county legislation
- Can enter into contracts with other county Governments as a guide under Article 189(2) of the constitution. This can be through the management of county resources
- Counties can establish various Public offices and manage their resources, including making appointments to those offices and exercising discipline if the person violates laws of conduct and the Constitution
- County governments can enter contracts, acquire, purchase, or lease land, delegate functions, and partner with public and private organizations.
Administrative Hierarchy of County Government
Like the national government, which operates under 3 arms (executive, Judiciary, and legislature), the county government also has 3 arms that allow it to work and better serve its members. They are:
County Executive Committee
The highest hierarchy of all county governments in Kenya is the County Executive Committee. These committees include the Governor (Head of the county), the deputy governor, and members appointed from the county assembly. Lastly, there is the county secretary who heads the county Public service.
County Assemblies
Second in command are the county assemblies, which are made of MCAs elected to represent the various wards in the counties. They function the same way as the National government parliament and pass laws and bills to determine how the countries operate.
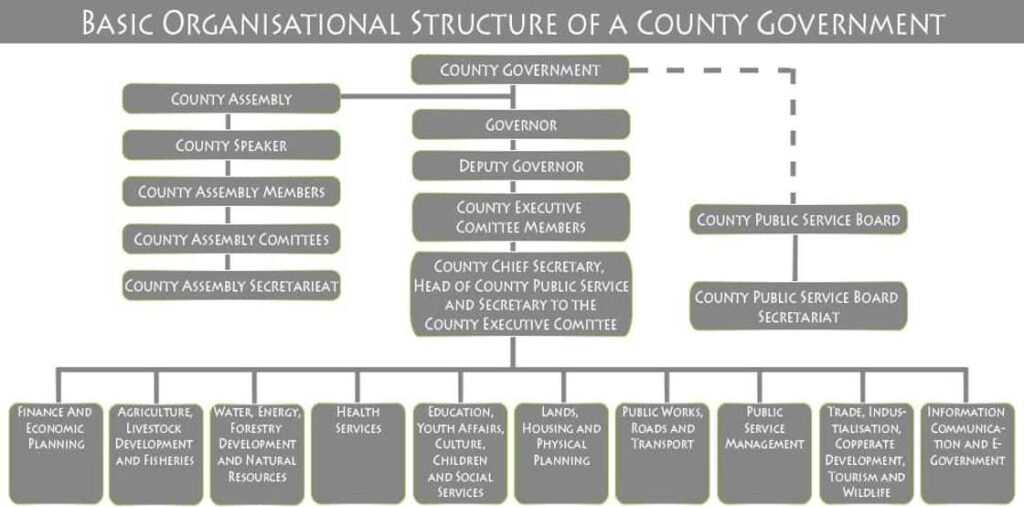
County Public Service
Enter the county public service to ensure that the County government can deliver and serve the general public. This arm is mainly concerned with the county government employees who are involved with delivering county services. The county, through public services, usually advertises various vacant positions, and members of the public can apply for and fill these positions.
What is the population of each county in Kenya?
The National Bureau of Statistics census every 10 years in Kenya determines the number of Kenyans in the country. In the last census, which took place in 2019, Knya had a total population of 47,558,296 inhabitants. Out of this, Nairobi county had the highest number of people with a total of 4,397,073 and Lamu the last with a total of 143,920 persons living in the county
Below is a population table that shows the population of all 47 counties from the 2019 census data:
| Code | County | Population (2019 census) |
|---|---|---|
| 001 | Mombasa | 1,208,333 |
| 002 | Kwale | 866,820 |
| 003 | Kilifi | 1,453,787 |
| 004 | Tana River | 315,943 |
| 005 | Lamu | 143,920 |
| 006 | Taita–Taveta | 340,671 |
| 007 | Garissa | 841,353 |
| 008 | Wajir | 781,263 |
| 009 | Mandera | 867,457 |
| 010 | Marsabit | 459,785 |
| 011 | Isiolo | 268,002 |
| 012 | Meru | 1,545,714 |
| 013 | Tharaka-Nithi | 393,177 |
| 014 | Embu | 608,599 |
| 015 | Kitui | 1,136,187 |
| 016 | Machakos | 1,421,932 |
| 017 | Makueni | 987,653 |
| 018 | Nyandarua | 638,289 |
| 019 | Nyeri | 759,164 |
| 020 | Kirinyaga | 610,411 |
| 021 | Murang’a | 1,056,640 |
| 022 | Kiambu | 2,417,735 |
| 023 | Turkana | 926,976 |
| 024 | West Pokot | 621,241 |
| 025 | Samburu | 310,327 |
| 026 | Trans-Nzoia | 990,341 |
| 027 | Uasin Gishu | 1,163,186 |
| 028 | Elgeyo-Marakwet | 454,480 |
| 029 | Nandi | 885,711 |
| 030 | Baringo | 666,763 |
| 031 | Laikipia | 518,560 |
| 032 | Nakuru | 2,162,202 |
| 033 | Narok | 1,157,873 |
| 034 | Kajiado | 1,117,840 |
| 035 | Kericho | 901,777 |
| 036 | Bomet | 875,689 |
| 037 | Kakamega | 1,867,579 |
| 038 | Vihiga | 590,013 |
| 039 | Bungoma | 1,670,570 |
| 040 | Busia | 893,681 |
| 041 | Siaya | 993,183 |
| 042 | Kisumu | 1,155,574 |
| 043 | Homa Bay | 1,131,950 |
| 044 | Migori | 1,116,436 |
| 045 | Kisii | 1,266,860 |
| 046 | Nyamira | 605,576 |
| 047 | Nairobi | 4,397,073 |